>

Basal reinforced embankments
Embankments on soft soil
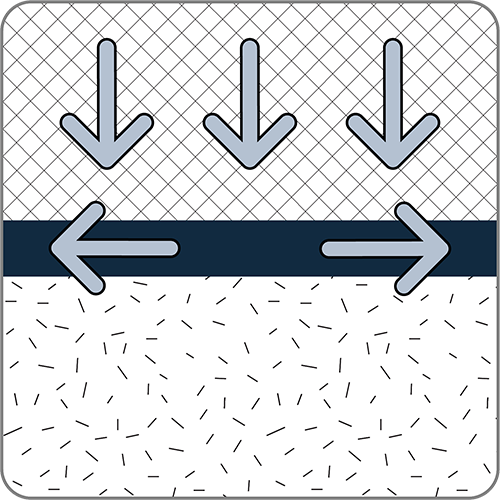
The stability of embankments on soft soils can be enhanced by the use of geosynthetic reinforcement layers installed in the embankment contact zone. The benefits of this usage include higher stability due to providing tenacity, less time dependency on consolidation, and a more uniform settlement behavior of the construction. It enables the embankment to be constructed higher, and with steeper side slopes, than would be the case if no reinforcement was used.
Piled embankments
A geosynthetic-reinforced earth structure over vertical bearing elements (piles) refers to a single- or multi-layer composite structure made of soil layers and geosynthetic reinforcement elements, which rests on natural, soft ground and the bearing element. The geosynthetic reinforcement has two main purposes: Firstly, it bridges the soft soil between the piles and activates a mechanism to support a direct stress distribution from the embankment and traffic loads into the piles. Secondly, is provides additional stability to the embankment. This enables the embankment to be constructed to any height, at any rate, without instability and settlement problems.
Reinforcement over cavities
Collapses are represented by crater-like subsidences on the ground surface, generally appearing suddenly. They occur through the collapse of subterranean cavities, growing upwards in time until they finally break through the surface. In areas prone to subsidence hazards, preventive stabilization for civil structures such as new roadways is required. Geosynthetic reinforced earth structures being used below the transport route subgrade are an adequate technique to overbridge the endangered zone, ensuring foundation void formation does not lead to distress at the surface of the embankment. Temporary as well as permanent safety concepts using geosynthetic reinforcement are possible.